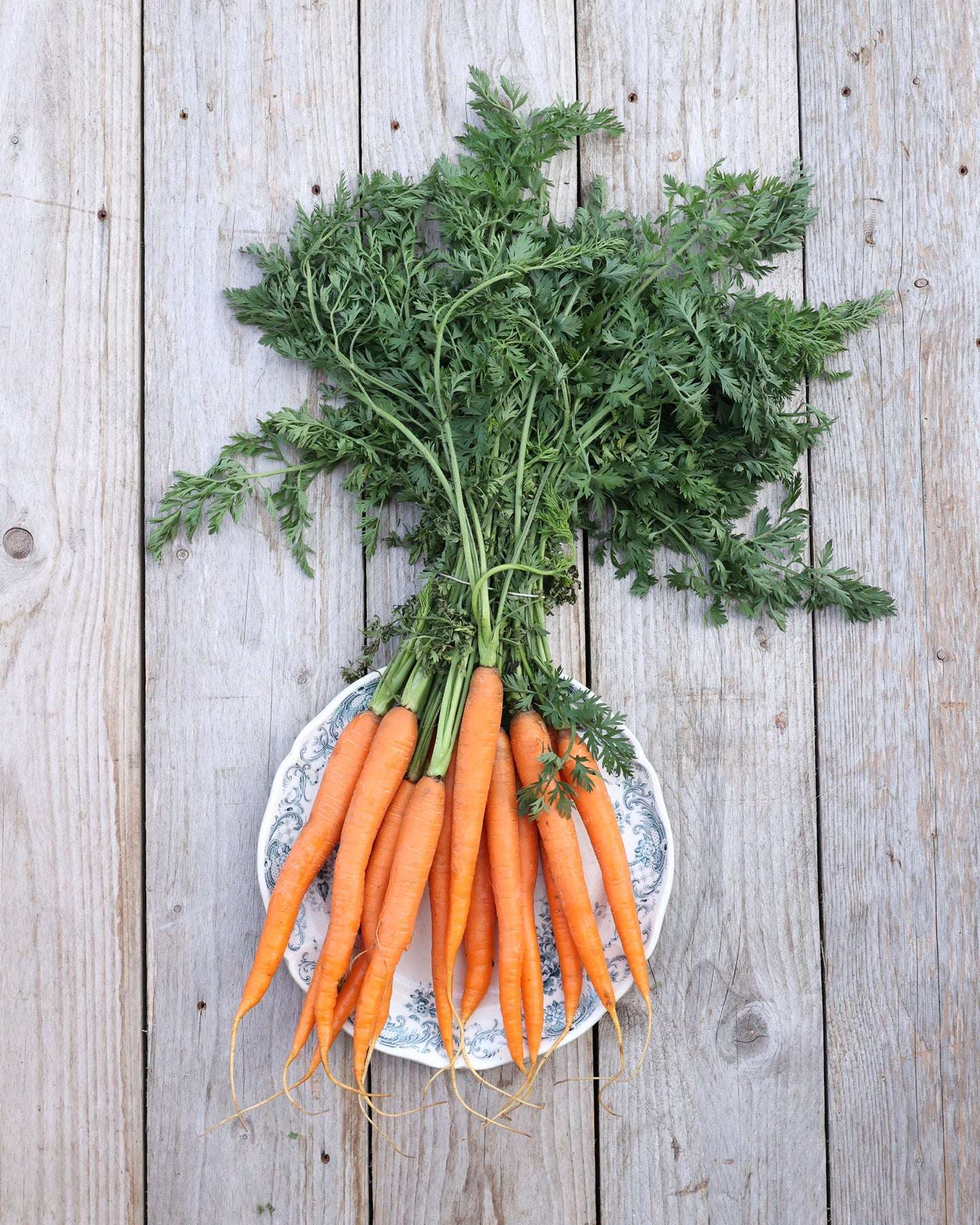
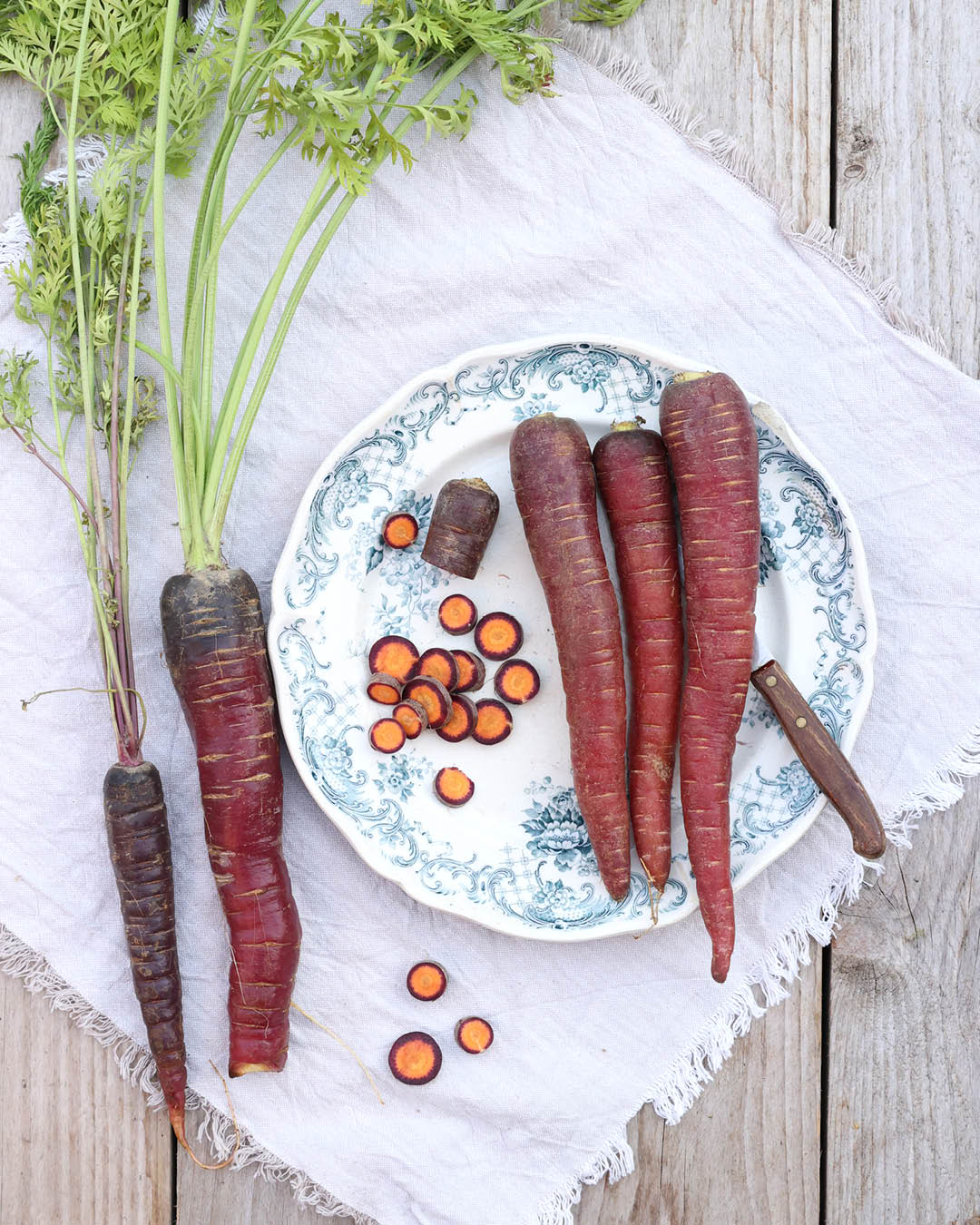
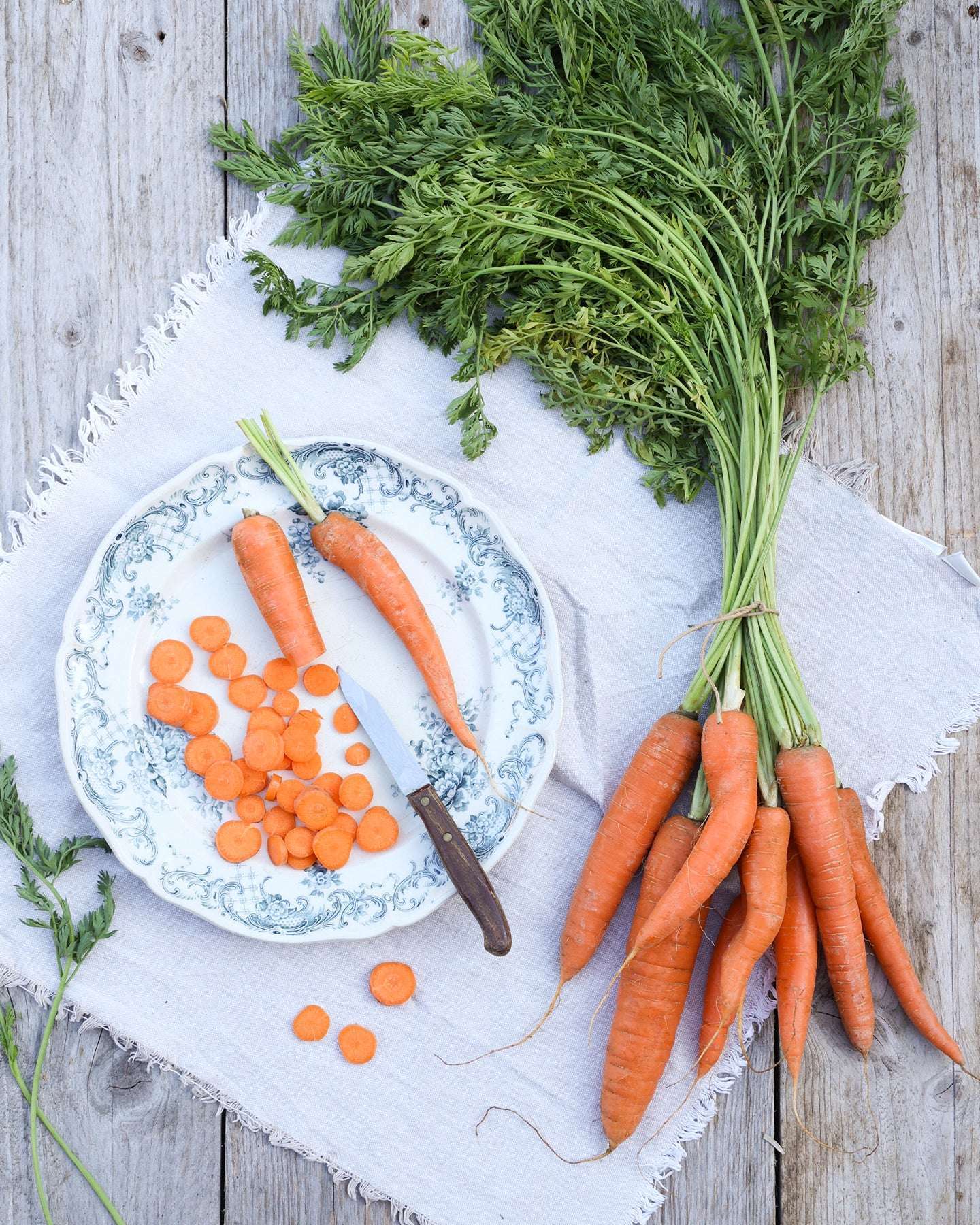
Carrots
The colorful beet plant is an all-rounder among vegetable plants and offers a wide variety of varieties. Carrots grow particularly well in light, loose soil, both in the ground and in pots. If you want to enjoy the taste of this crunchy vegetable all year round, plant different varieties and admire the variety of shapes and colors of beets.

Planting time – When is best?
Depending on the region, sowing takes place between March and June. Early beet varieties are sown in February to March, summer varieties from March to April. Winter varieties should be sown later, in June and July.
Growing carrots – How does it work?
First, you should loosen the soil and then create seed furrows about two centimeters deep. The distance between the furrows should be about 20 cm. Now you can sow the seeds about five millimeters apart, then cover them with a thin layer of soil and press them down firmly. Afterward, you should water the seeds well with a sprinkler, as otherwise the germination time will be very long. Depending on the variety, the plant should be thinned out to a distance of four centimeters once it has two to three leaves. The space required, however, varies from variety to variety. To avoid infestation by the carrot fly, it is better to fill the resulting cavities with some soil. Sowing coriander next to the carrots can also protect against these pests.
Location – Where is best?
Light, loose, and humus-rich soils are best suited for growing beet plants. Growing them in pots is also possible. However, a successful harvest requires relatively high soil moisture and a moderate climate. Tip: Plant carrots in raised beds. Carrot flies cannot fly higher than 30 cm, so they have no chance.
Care – What needs to be done?
Regular watering is important during cultivation. However, don't overdo it, or you'll end up with lush foliage, which is detrimental to the roots. Weeding is best done at dusk, as the scent of the leaves can attract carrot flies. Also, hoe regularly between the rows to loosen the soil.
Harvest – What should you consider?
The early varieties can be harvested as early as April and May, reaching a finger-thickness. Long-season varieties, on the other hand, require four to five months of ripening and will then have reached a diameter of approximately four centimeters. The last carrots should be harvested in November. Carrots are best stored without leaves in a cool, dry, and dark place.
Mixed culture – to good neighbors!
Green peas, beans, lettuce, dill, onions, garlic, leeks, chamomile, as well as marigolds and marigolds are ideal companion plants for carrots. Avoid planting them near beets.
Botany – What kind of plant is this?
This root vegetable belongs to the Umbelliferae family and is a biennial plant. However, it is cultivated only as an annual in gardens. Carrots should be grown for at least three years.
Carrots come in a wide variety of shapes and colors. Depending on the variety, the root can be short, medium-long, long, cylindrical, top-shaped, or conical. The color spectrum ranges from light or dark red, orange, white, to violet, which is due to the substances carotenoids, anthocyanins, and chlorophyll.
Cultural history – How did the carrot come to us?
The ancestor of today's garden carrot originates from parts of Europe, North Africa, and western Asia and is known as the "wild carrot." This carrot was white-yellow and less sweet than today's carrot. Finds show that this species probably served as food for hunters as early as the Stone Age.
Over time, different carrot varieties developed in different regions of the world. In Central Asia, they were mostly purple, while in the Mediterranean region, they tended to be yellow and white. The development of today's cultivated carrots probably began in the 17th century through targeted breeding in the Netherlands. From this time on, the carrot also acquired its characteristic orange color and sweet flavor.
From there, the vegetable spread throughout the world, displacing other, more ancient root vegetables such as parsnips and sugar beet.
Today, depending on the region, the carrot is also known in Germany as “carrot”, “yellow carrot”, “root” or “Rübli” and is an important source of vitamins for a balanced diet.
TEXT: Merle Hildebrandt